Category: General

2026 Nissan Leaf details: Affordable EV will face 2026 Chevy Bolt EV
- Next-generation Nissan Leaf will launch first in U.S. and Canada, be fully revealed this year
- Rogue Hybrid and Rogue PHEV are on the way over the next two model years
- A broader range of U.S.-made Nissan and Infiniti EVs starts to arrive in 2028
Affordable EVs? Widely available hybrids? A plug-in hybrid? As it emerges from financial upheaval, Nissan on Monday announced several intriguing product surprises relating to the North American market that altogether may bring a breath of fresh air to its U.S. lineup. .
Firstly, the Leaf is definitely U.S.-bound, and it’s coming here first. Nissan confirmed that the next-gen Nissan Leaf will launch initially in the U.S. and Canada—actually before Japan, and before Europe. It’s due to be fully revealed this year, but it and a 2026 Nissan Rogue plug-in hybrid, which will use a version of the system in the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, will arrive in fiscal year 2025, meaning later in 2025 or by March 31, 2026.
The timing announcement came at the same time as a first teaser photo of the next-generation Leaf. As anticipated it shifts to a more elevated seating position and a more crossover-like profile, closely cribbing the 2021 Chill-Out concept that Nissan itself said from the start was a hint of the next Leaf. Nissan more recently teased that the Leaf gets a Tesla NACS port in U.S. form, too.
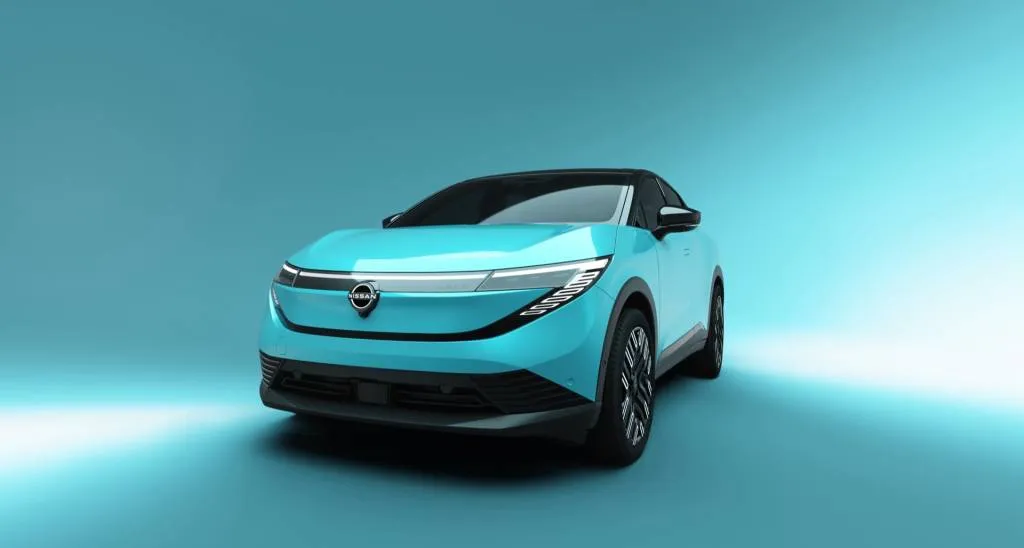

2026 Nissan Leaf teaser
Nissan has also said that the next Leaf will be liquid-cooled and load up on some of the technology from the excellent Ariya, and be more competitive in range and efficiency. With that, plus its stylish new look and what we have to assume will remain an attractive price, it will arrive just in time to take on the next-generation 2026 Chevy Bolt EV—which will shift to LFP batteries and, as a GM executive boasted last year, will be the most affordable U.S. EV. As of GM’s last update, the Bolt EV is also due later this year.
In the same timeframe, by early 2026, Nissan will launch a new generation of its Sentra compact sedan, as well as a refreshed Pathfinder SUV. It hasn’t yet said if hybrid powertrains are in the works for either of these models.
Then in fiscal year 2026—meaning by March 31, 2027—Nissan will start making a completely new generation of the Rogue for the U.S. and Canada. This one will not only continue to take advantage of the plug-in hybrid powertrain in some versions of the Rogue but also, as it promised earlier this month, finally take advantage of Nissan’s e-Power series hybrid tech in other Rogue versions.
Given previous remarks from Nissan executives, Green Car Reports expects the Rogue Hybrid to be a widely available volume model in the lineup, not a niche offering.
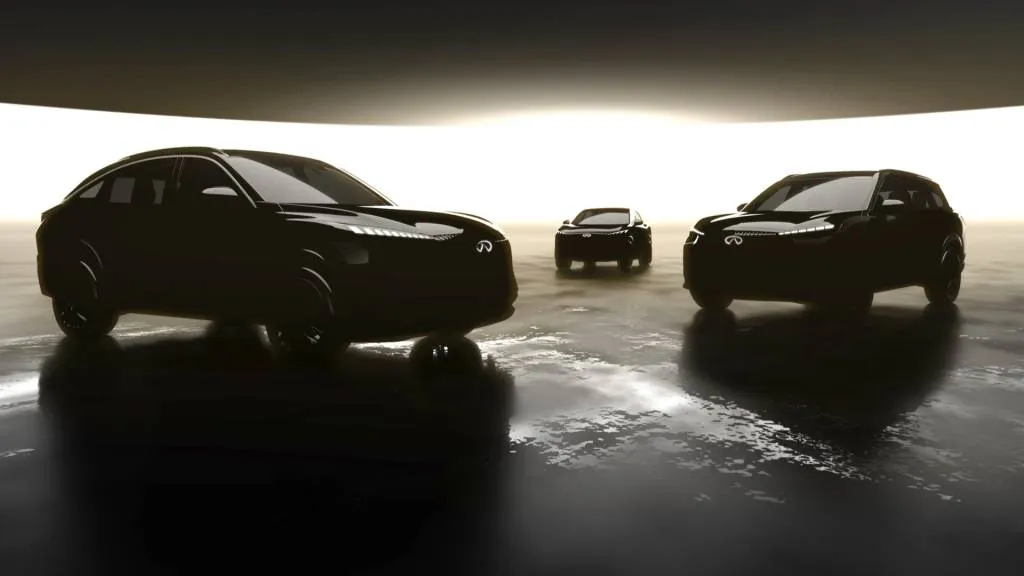

Future Infiniti U.S. EV lineup
In early calendar year 2028 Nissan is expected to ramp up production of “an adventure-focused SUV”—at its Canton, Mississippi, plant, with an Infiniti electric SUV following later that year. Nissan notes that the Infiniti EV will be inspired by its Vision QXe concept that made its debut just before the 2023 Tokyo auto show and premiered a new Artistry in Motion design direction. At that time Infiniti said that the low-set QXe previewed a “sleek sedan” set to be made at Canton, so it’s unclear whether that’s still on the way or replaced by an SUV.

Rivian spinoff focuses on small EVs, “ways to move beyond cars”
- Spinoff starts with $105 million VC investment, Rivian maintains “substantial minority stake”
- Products to be affordable, vastly more efficient than today’s cars or SUVs
- In-house-built for core components, may share sales space with Rivian
- Flagship product coming in early 2026
Do we really need a new generation of EVs that are bigger and heavier than equivalent gasoline trucks and SUVs, and the so-called segment creep that continues to make each successive U.S.-market vehicle larger than predecessors?
These are tough, societal questions without easy answers, and it involves a tangle of regulations, consumer habits, and the limits of affordable technology. But a Palo Alto, California–based micromobility startup being spun off by Rivian, called Also, looks like it aims to tackle them—and, from the sound of it, give American consumers a way to just say no to those super-size products.
In a press release announcing the venture, which Rivian had previously kept under wraps, Rivian clarified that it maintains a “substantial minority stake” in Also and “expects opportunities for future collaboration, which may include selectively using some of Rivian’s retail footprint.”
With the spinoff of the company Also secures a $105 million investment from the VC fund Eclipse Ventures, and Rivian CEO RJ Scaringe will serve as its chairman and on its board of directors.
Also, in a page about the company, says that it will launch its flagship product in early 2026 and will initially focus on the U.S. and Europe prior to global expansion.

Rivian R3
That product will be part of an entire range of “exciting, small EVs,” according to Also, that will be built on a vertically integrated technology platform. With everything built for the platform in-house, including motors, batteries, electronics, and software, Also claims “a user experience that is unlike anything seen in these segments before.”
“Also is building an exciting range of electric vehicles that are efficient, sustainable, and delightful to use,” the company sums.
In job postings, Also quantifies its product targets a little bit. “Our mission is to inspire everyone to ride also—replacing many local car, truck and SUV miles with ones on vehicles that are more affordable, more enjoyable and 10-50x more efficient.”
Road transportation is the leading contributor to global CO2 emissions, Also says, while 80% of car trips are 15 miles or less and half are under 6 miles.
Rivian continues to also set its sights toward significantly smaller vehicles than its own flagship R1T electric pickup and R1S electric SUV. Its upcoming $45,000 R2 electric SUV is on the way in 2026, while it’s also working on smaller Rivian R3 and R3X rugged hatchbacks that are set to follow. All of this comes in addition to the $5.8 million VW-Rivian joint venture that will result in a new Rivian-based zonal architecture for future VW Group EVs.

Here are the EVs made in Mexico and Canada
- Auto-industry tariffs coming in April, may bring immediate price hikes
- Mexico makes many U.S.-bound EVs, buys few of them
- EV tax credit still potentially applies to models made in Mexico and Canada
The threat of auto tariffs affecting models made in Mexico and Canada has not abated. And as industry experts continue to suggest, there may be rocky times ahead for vehicle affordability.
Although delayed, the auto-industry tariffs are coming soon, as are additional tariffs on China and the EU, President Donald Trump revealed Monday.
“We’ll be announcing that fairly soon, over the next few days probably,” said Trump, as quoted by Politico. “And then April 2 comes. That will be reciprocal tariffs.”
According to the report, the U.S. imported $471 billion in automotive products in 2024, which includes $214 in passenger cars.
Mexico builds many U.S.-bound EVs but buys few of them—and EVs are a very small portion of the nearly 1.1 million new cars sold in Mexico. A lack of significant charging infrastructure, combined with affordability, remain obstacles.
That’s because EVs generally remain too expensive for that market—although Mexico has in recent months announced plans to develop its own EV supply chain as it’s also pushing ahead with a federally subsidized EV that might cost as little as $4,400.

2025 Chevrolet Blazer EV
Under the Biden-era Inflation Reduction Act, tax credits of up to $7,500 stipulated requirements for North American assembly and sourcing, in policy that went along with the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) deal made during the first Trump term and closely following NAFTA policy that preceded it. Trump has separately indicated a desire to eliminate the EV tax credit, which a research group recently emphasized would have a devastating effect on U.S. manufacturing.
Mexico currently builds hundreds of thousands of U.S.-bound vehicles annually—many of them affordable entry-level models. Automakers have already cautioned that tariffs on Mexico and Canada would lead to immediate price hikes in some cases, as well as the potential for some models to be pulled from the market.
According to a Reuters report from December, citing estimates from Wells Fargo, a 25% tariff on parts from Canada and Mexico would make vehicles more expensive, EV or not. Specifically, it might add $2,100 in cost to consumers for U.S.-assembled vehicles alone, while models made in Canada or Mexico could end up costing $8,000 to $10,000 more.
It could affect the viability of some of the domestic automakers as well. GM is relying on imports from Canada and Mexico for both profitable full-size trucks and various EVs. Mexico Business News noted that GM alone assembled more than 889,000 vehicles in Mexico, with about 653,000 of those shipped to the U.S.

2025 Ford Mustang Mach-E Rally
EVs from Mexico
As called out by the latest list from the federal government per American Automobile Labeling Act (AALA) labeling requirements, here are the plug-in models currently made in Mexico:
Ford Mustang Mach-E (EV)
Cadillac Optiq (EV)
Chevrolet Blazer EV
Chevrolet Equinox EV
Honda Prologue (EV)
Jeep Wagoneer S (EV)
Audi Q5 S line 55 e (plug-in hybrid)

2024 Dodge Charger Daytona
EVs from Canada
Dodge Charger Daytona EV

2025 Honda Civic Hybrid
Hybrids from Canada
And here are the hybrids, including several plug-in hybrids, made in Canada:
Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid (plug-in hybrid)
Civic Hybrid 5-dr
Lexus RX350h
Lexus RX500h
Toyota RAV4 Prime (plug-in hybrid)

Southern US states are set for the most EV range, data suggests
Extreme temperatures can affect electric vehicle range, but the extreme heat of the South is nothing to offset the extreme cold in other parts of the U.S., according to new findings.
Vaisala, a Finnish instrumented measurement firm, analyzed the effect of weather and road conditions on EV range across the Lower 48 states, looking at how these factors affected range at different times of the year. That analysis involved not only temperature by month, but also winds, rolling resistance from snow, air density, and solar radiation, among other factors.
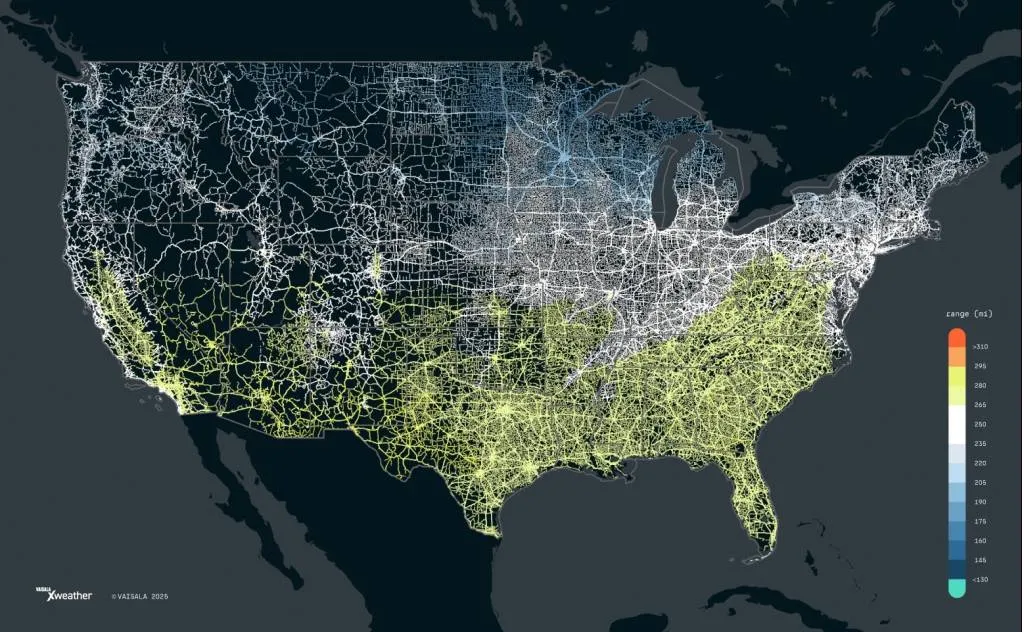
EV range based on climate in U.S. states (via Vaisala)
States at lower latitudes, with hotter average temperatures, showed better results. The top five states for EV range, based on a median and across all local climatic conditions were Arizona, Florida, Texas, Georgia, and Louisiana. The bottom five were the more northern—and frigid—Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, North Dakota, and Minnesota.
Analysts also compared the median-range findings to rates of EV adoption in each state. Some of the states with the most ideal conditions for EVs have the lowest adoption, and vice versa. Further, California is a surprise; although tops in EV adoption, it doesn’t actually have ideal conditions for maximizing range.
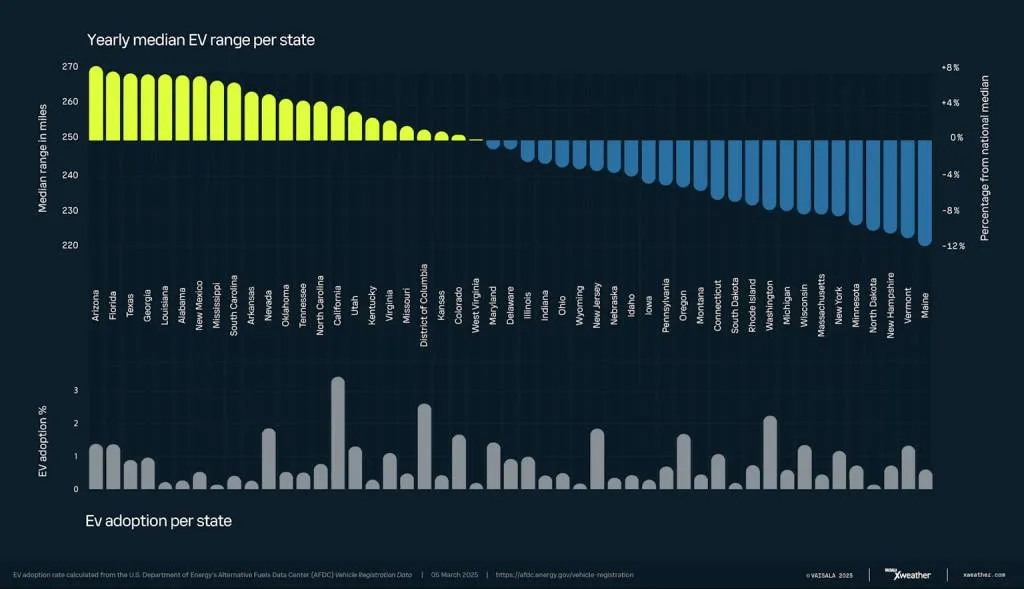
EV range based on climate in U.S. states (via Vaisala)
Florida, however, is second only to California in EV sales. And Texas ranks especially high in EV sales as well. Those two states—and some others with high EV adoption rates—don’t have sales mandates or strong incentives for them, either.
The pattern here also doesn’t follow the states that have adopted California’s EV mandate, which tend to be in the colder, northern parts of the country where weather appears to affect EV range more. Although Connecticut and Maine, a couple of the most challenging states according to the data, have delayed adopting the mandate.

GM-Pilot EV charging network now spans over 25 states
- GM-Pilot stations with EVgo now cover more than 130 locations
- The automaker also has GM Energy projects with ChargePoint and EVgo
- GM is also part of Ionna, seeking 30,000 fast-chargers by 2030
Automakers beyond just Tesla have been committing to the EV infrastructure buildout; and among them, General Motors remains one of the most diversified in this push.
Tuesday, GM and Pilot Company, with the charging network EVgo, confirmed in an update that it’s been pushing ahead with its installation of electric vehicle fast-charging stations, with more than 130 locations now available in over 25 states.
The three partners originally announced plans in 2022 to install up to 2,000 EV fast-charging stalls at 500 different travel center locations, where road-trippers can also enjoy lounges, free wi-fi, various food and beverage options, modernized restrooms, and 24/7 staffing. The GM-Pilot network, with CCS connectors up to 350 kw, now covers I-75 from Michigan to Georgia, as well as several other regional corridors in the South and Midwest.
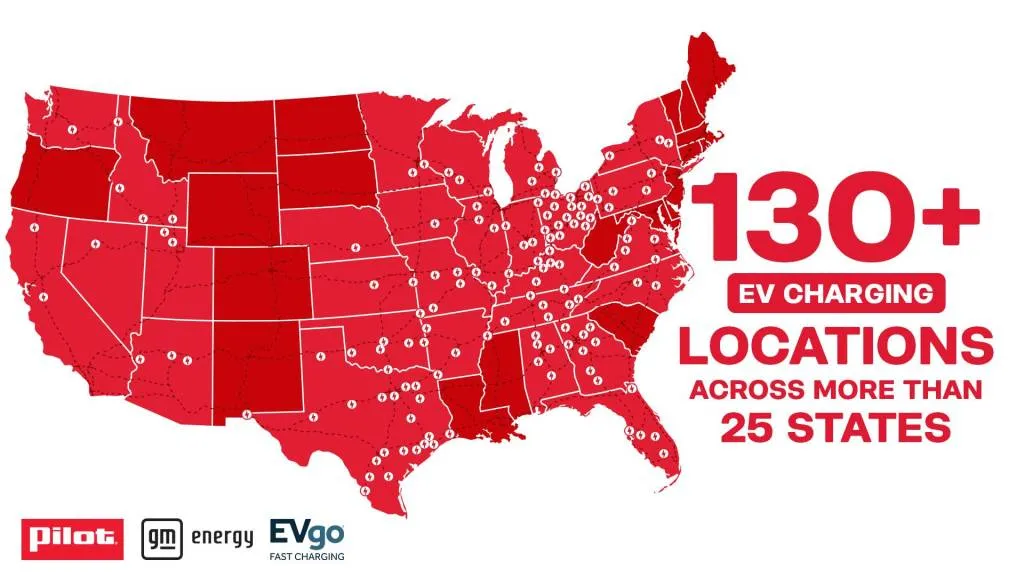
Pilot, GM, and EVgo build out EV fast-charging network
That was before the formation of the U.S. EV fast-charging network Ionna. That network has been backed by General Motors, BMW Group, Honda, Hyundai, Kia, and Stellantis from the time of its inception in 2023, with Toyota since joining. The proposed scale of that network—targeting 30,000 chargers by 2030, or roughly the same number Tesla has today—appears like it might be the first true rival to Tesla and its Supercharger network. Each piece of Ionna hardware can charge at up to 400 kw for one vehicle or split that for up to 200 kw for two vehicles and is plug-and-charge compatible.
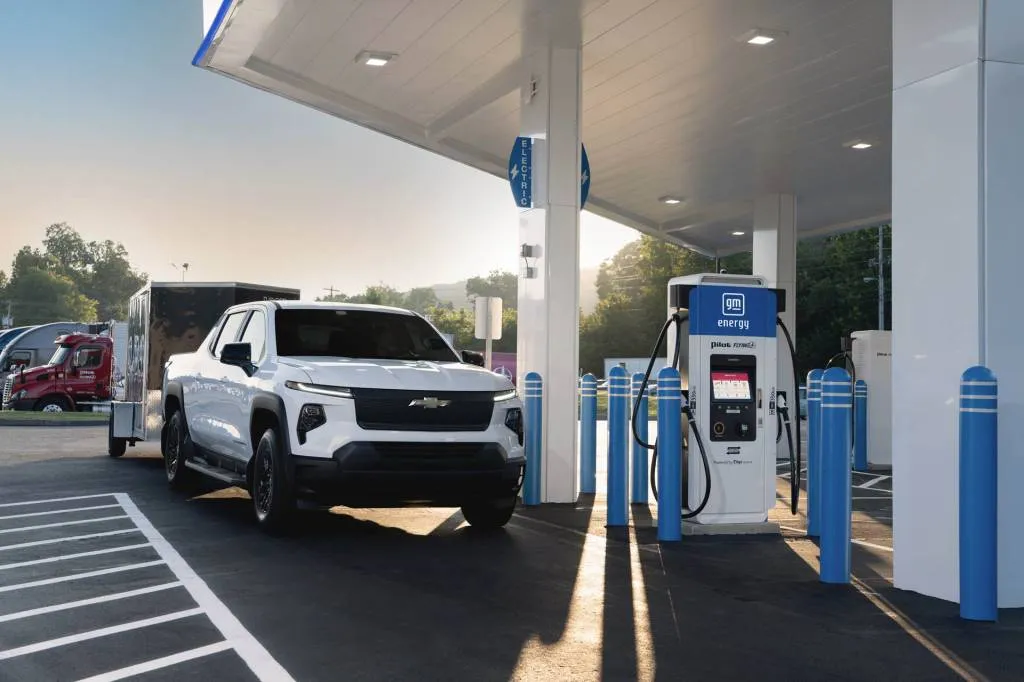

GM and Pilot Company’s EV charging network
Tuesday’s announcement and the deployment with Pilot and Flying J don’t encompass all that GM and EVgo are doing together. As part of plans to install 2,850 charging stalls together, GM and EVgo also last September revealed plans for gas-station-like urban “flagship” EV charging sites with 350-kw connectors, in major U.S.-metro areas starting in 2025. Meanwhile, GM and ChargePoint are rolling out 500 DC fast-chargers at up to 500 kw each, utilizing ChargePoint’s OmniPort adapter encompassing CCS and NACS standards. Both of those latter efforts will be co-branded with GM Energy.
As a recent Consumer Reports survey suggested, drawing from good and bad feedback from thousands of charging sessions, users of third-party networks such as EVgo, Blink, and Shell Recharge encounter more than ten times the issues vs. Tesla and its Supercharger network. But with automakers more closely involved—like GM with these efforts—we look forward to seeing them smooth things over.

Sulfur-crystal battery could triple EV range without cobalt or nickel
A German startup believes it has the recipe for electric vehicle battery cells that are cheaper, more energy dense, and less problematic for the environment than current lithium-ion cells. But commercialization seems a long way off.
Theion announced Thursday in a press release that it is close to completing a 15 million euro (approximately $16.2 million at current exchange rates) Series A round to development of its sulfur-crystal battery chemistry. It’s based on proprietary anode technology that Theion hopes will extend battery life—one of the main obstacles to sulfur-based chemistries.

Theion sulfur-crystal EV battery development
With this chemistry, Theion is aiming for energy density of 1,000 Wh/kg, which is about triple that of leading-edge nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) cells today, including the 4680 cells used in the Tesla Cybertruck. Such energy density would allow for much lighter cells without sacrificing range, or increased range from the same volume.
Theion claims it can achieve this without using nickel or cobalt, addressing environmental and human-rights concerns associated with the mining of those metals. Overall, Theion claims its cells could have a one-third lower carbon footprint—and cost—compared to conventional cells. That’s because, as the firm notes in its release, sulfur is the 16th most abundant element on Earth, and costs much less than the raw materials of NMC cells.

Stellantis STLA Medium platform
But as Theion emphasizes, longevity in cycle life will be the challenge for sulfur-crystal batteries. The startup believes its batteries need to maintain performance over 1,000 charge/discharge cycles to be commercially viable, a target it aims to build up to, after initial testing of 500 Wh/kg cells at 500 cycles, before starting production.
Research into lithium-sulfur batteries for EVs goes back at least a decade, and we’ve seen impressive claims about their ability to boost EV range before. Stellantis has even partnered with not one, but two startups—Lyten and Zeta Energy—that aim to commercialize the tech, perhaps by the end of the decade. But it remains to be seen if any of these efforts—Theion’s included—will overcome the hurdles and get sulfur batteries into production EVs.

California has nearly 50% more public EV chargers than gas nozzles
- In 2024, public charging in California expanded at record levels
- The state has double the publicly accessible chargers versus 2022
- Nearly 30% of U.S. EV sales go to California customers
In California, drivers are now much more likely to encounter an electric vehicle charging connector than a gas pump nozzle.
The state reached 178,549 public chargers in 2024 (including shared private chargers), Governor Gavin Newsom’s office announced Thursday in a press release. That gives California 48% more publicly accessible chargers than gas pumps, according to the California Energy Commission (CEC), which estimates about 120,000 gas pumps in the state.
Installation of new chargers has increased significantly over the past few years. California now has twice as many publicly accessible chargers as it did in 2022, and it added 26,193 chargers since the last official update of the total in August.
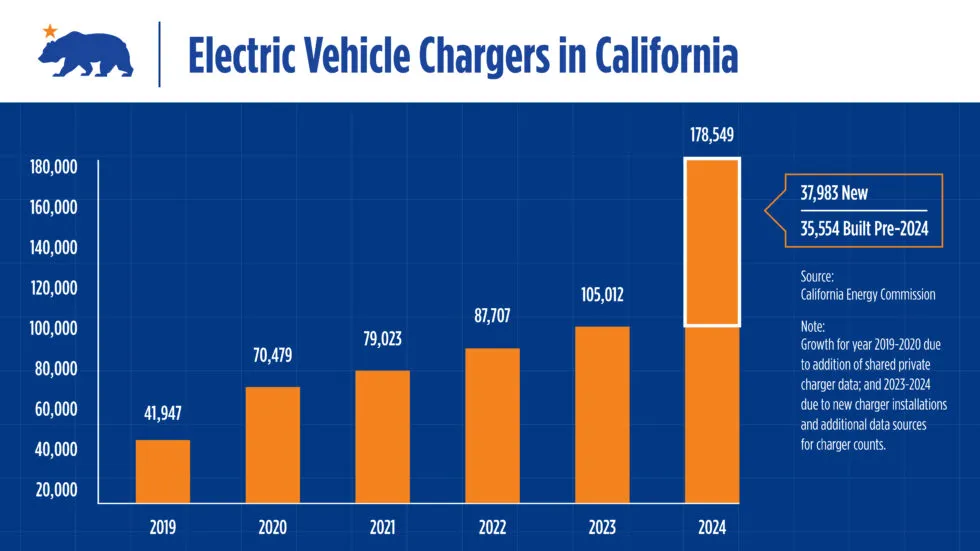
Electric vehicle chargers in California in 2024
While California continues to devote funds to building more charging stations, part of the increased total for 2024 is due to keeping better track of ones that already exist. Of the 73,537 chargers added to its data set in 2024, 35,554 were installed before that year but were newly identified through additional data sources, according to the CEC.
Publicly accessible chargers are mostly Level 2 AC, at over 162,000, with nearly 17,000 DC fast-chargers, according to the CEC. The commission also estimates that more than 700,000 Level 2 chargers are installed at single-family homes in California for private use.
Those chargers—public and private—support what remains the largest fleet of EVs in any U.S. state. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) estimates that nearly 30% of U.S. “zero-emission vehicle” sales go to the state.
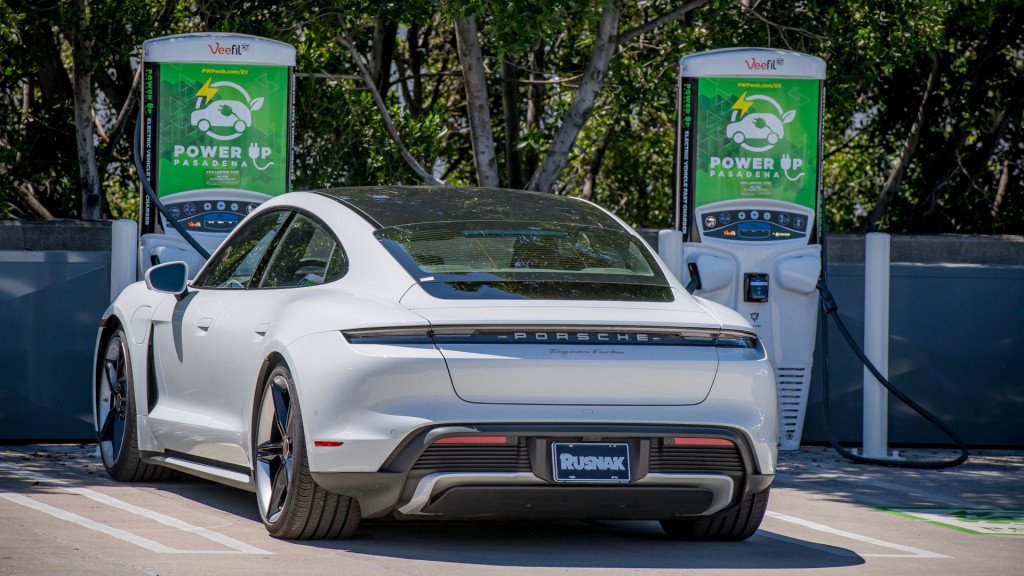

Marengo Charging Plaza, Pasadena, California
California may also bring back its own version of an EV tax credit—minus Tesla—if the federal credit is cut, something the Trump Administration is reportedly preparing to do. The Biden EPA officially approved restoration of California’s EV sales mandate prior to an expected Trump attack on the state’s rights, but the new government may still hold California’s solo carpool-lane access for EVs hostage.
In the meantime, California is also pushing ahead with its charger buildout as Trump freezes federal charger funding. Last month California announced a $55 million project, overseen by the CEC, supporting the installation of DC fast-charging stations at retail sites throughout the state. It’s a small part of a $1.4 billion EV charging and hydrogen program announced in December.
“We’re embracing our clean car future and providing consumers more choices—no matter what ‘big government’ mandates come out of Washington,” Newsom said in a statement.

Study: Tesla, Rivian charging networks have far fewer problems
- Owners report more than ten times the issues with Shell Recharge, EVgo, or Blink than with Tesla
- Rivian’s own charging network was second only to Tesla
- Hardware-related issues have become more prevalent than payment problems
Charging networks operated by Tesla and Rivian tended to have fewer problems than non-automaker efforts, according to a recent Consumer Reports survey.
Electric vehicle owners experience a problem in one out of every five public charging sessions, according to the survey, which draws from ongoing responses from CR’s EV Charging Community project.
In this edition, Consumer Reports includes information from about 5,700 total charging sessions, from 1,230 EV and plug-in hybrid owners. As CR notes to Green Car Reports, there’s not much variation in problems by U.S. region. But the rate of reported problems was certainly not uniform across all networks.
Survey respondents reported problems at Tesla charging stations 4% of the time, and 5% of the time at Rivian-operated chargers. In contrast, respondents said they experienced problems 48% of the time at Shell Recharge stations, 43% of the time at EVgo stations, and 41% of the time at Blink stations. It’s worth pointing out that all of these low-rated charging networks are third-party providers not directly owned or run by automakers
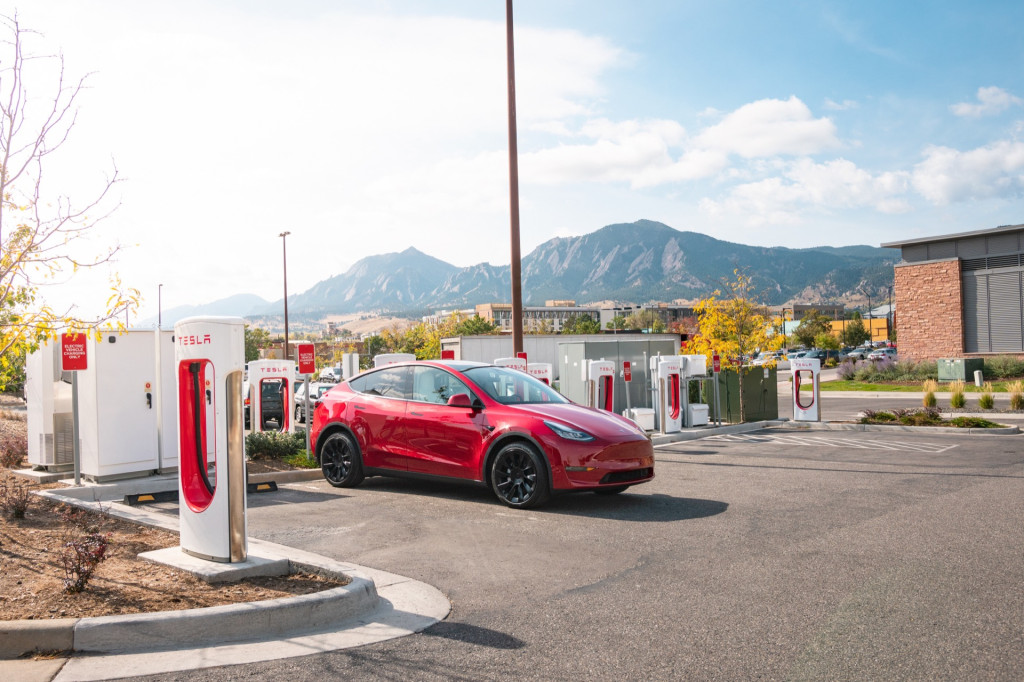

Tesla Supercharger
Rivian last year phased in a grading system for the charging experience via its route planner—so it appears that might be working. A J.D. Power study last year suggested Tesla Supercharging was losing its edge over other public charging, but this study suggests otherwise.
The most common reported problems were hardware-related, at 36%. “Other issues” accounted for 25% of the reported problems, followed by payment issues (23%) and charging power (15%). Payment issues used to be frequently cited as the most common issue EV drivers faced at public charging stations, so this is a notably different result.
Among the reported hardware problems, broken screens were by far the most frequent, at 76%. Other reported problems included damaged charging cables of connectors (10%), chargers that could not physically connect to a vehicle due to ice blockage, damage, or other issues (9%), and cables that were too short (5%).
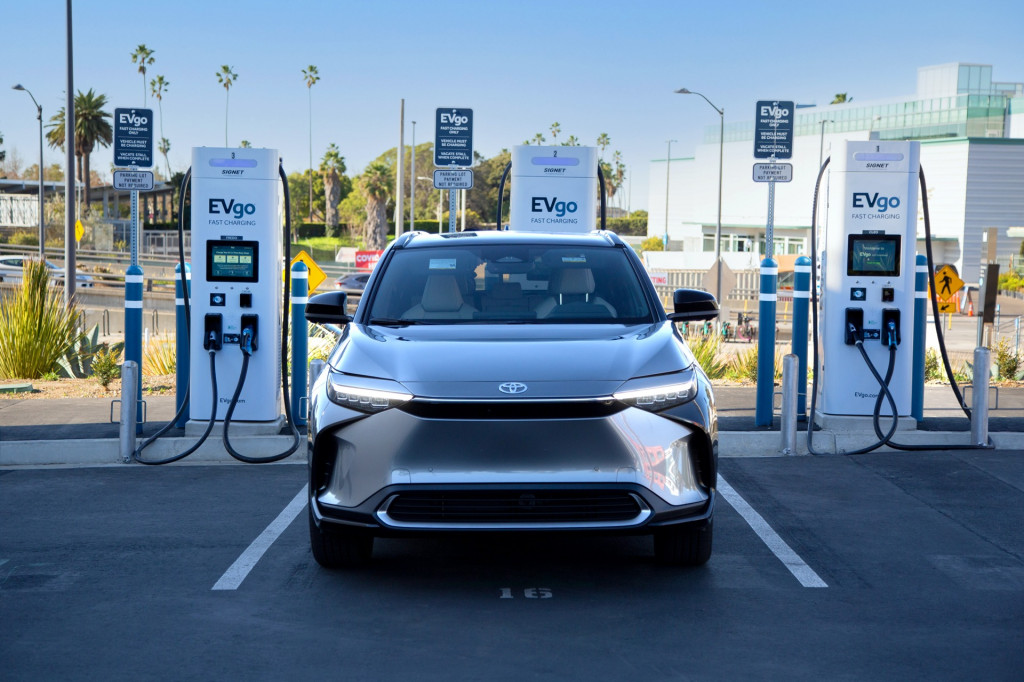

2023 Toyota bZ4X at EVgo charging station
Of those EV drivers who reported payment issues, 56% said they were able to pay but then encountered another issue that prevented them from charging; 25% said they were unable to pay at a given charger and had to move to another one; and 19% said charging never started despite payment being accepted.
To help make public charging go more smoothly, Consumer Reports recommends having multiple accounts with saved payment information so that, if there’s a problem with the charger’s interface, payment can be completed on a network’s app.
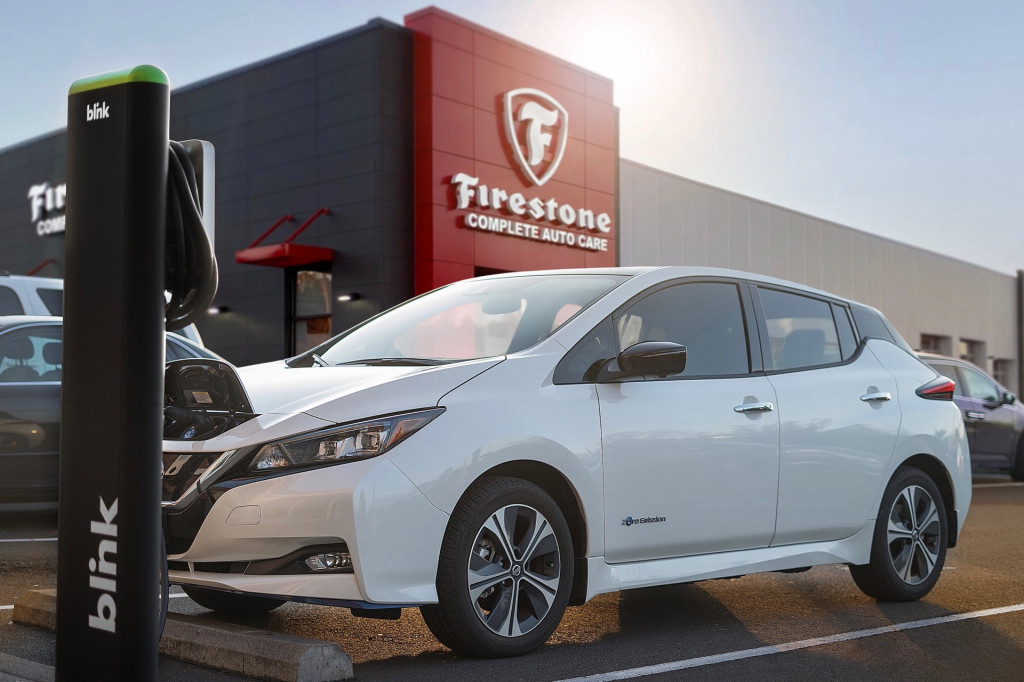

Blink Level 2 charging station at Firestone service center
General charging best practices, such as only fast-charging to 80% and preconditioning the battery pack before arriving, can help as well, the publication notes. In various polls and surveys, consumers continue to emphasize that the absolute charge rate doesn’t matter so much, rather that they get some level of charge in a reasonable amount of time.
With automaker-funded Ionna expanding rapidly, we’ll see how it lands on the scale of consumer approval—perhaps in a future update from this same data set.

EV battery recycling breakthrough recovers 99.99% of lithium
Chinese researchers claim to have developed a process to recover nearly all of the lithium from used electric vehicle batteries for recycling.
The Independent (via InsideEVs) reports on study results first published in the German academic journal Angewandte Chemie claiming recovery of 99.99% of lithium from a used battery, as well as 97% of nickel 92% of cobalt, and 91% of manganese.
The process used, called “neutral leaching” also eliminates harsh chemicals, increasing safety and lowering environmental impact, researchers claim—and in laboratory tests it took just 15 minutes to separate out the desired battery materials.
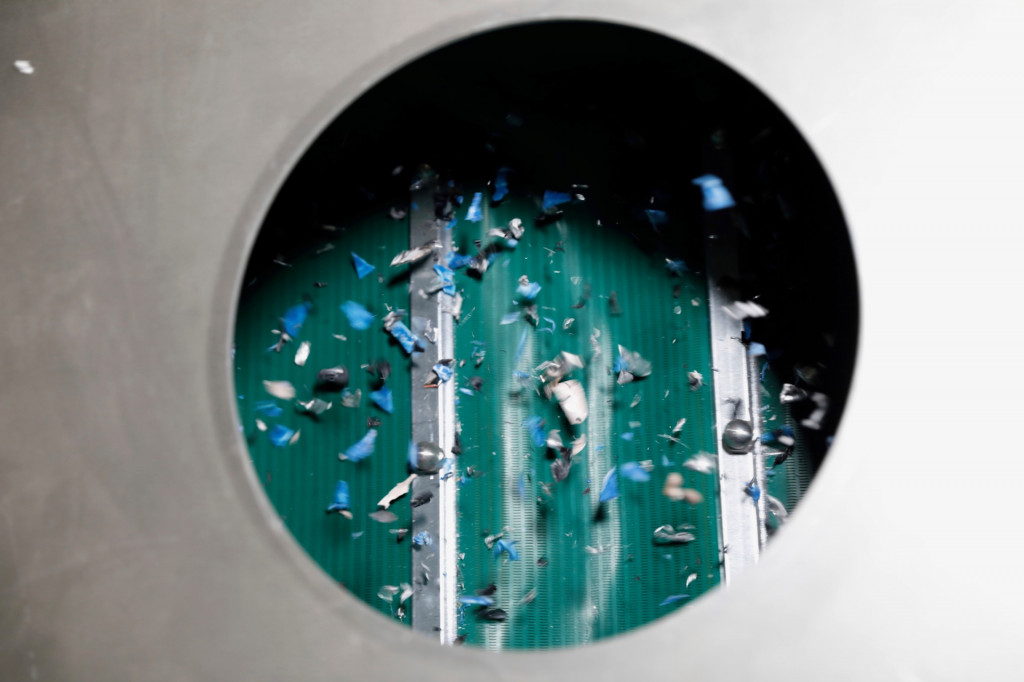

Volkswagen battery recycling
Current recycling processes use amino acids, and here study researchers used glycine, which is the simplest stable amino acid, along with a follow-up process to avoid further chemical reactions once the lithium and other materials were extracted.
Laboratory research does not always scale to commercial viability, but battery recycling has attracted interest from automakers looking to avoid the cost and the environmental impact of mining new raw materials for batteries.
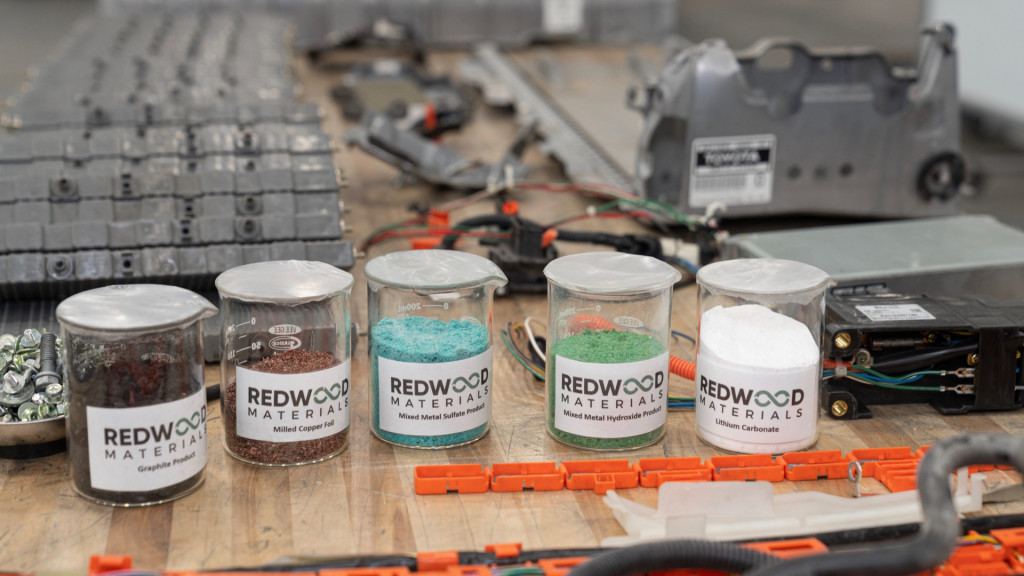

Toyota and Redwood Materials battery recycling
Toyota announced an agreement to utilize Redwood Materials, the battery-recycling firm founded by former Tesla CTO JB Straubel, in 2022. The following year, it expanded that agreement, setting the stage for batteries from hybrids like the Prius to provide material for future EV batteries as those vehicles reach the end of their useful lives.
Other automakers, including BMW, Ford, and Volkswagen Group’s VW and Audi brands, have also signed on with Redwood. But the fleet takes a long time to turn over, and the relatively small number of EVs and hybrids on the road could translate to a long wait for a critical mass of recyclable battery materials—with one 2021 report predicting that the market for these materials won’t heat up until 2030.

Rivian gear shop adds rooftop tent good for R1T or R1S
Rivian R1T and R1S owners can now buy a rooftop tent designed specifically for their electric vehicles.
Tent and camping gear manufacturer iKamper recently announced a special edition of its Skycap 3.0 Mini rooftop tent for Rivian, with mounting hardware keyed to the automaker’s trucks, an aerodynamic shell to reduce drag, and a Rivian-inspired color palette.

Rivian x iKamper Skycamp Mini rooftop tent
The tent itself can be pre-ordered for $4,595, and the first customers who do so will also receive iKamper’s Disco Series Stove for outdoor cooking. Rivian does offer a Travel Kitchen that can make breakfast for those who camp out, with a two-burner induction stovetop that can fit on an R1T’s open tailgate. It’s practical, but arguably not as cool as the Camp Kitchen, which slides out of the R1T’s Gear Tunnel pass-through, that the automaker showed at the truck’s media launch but never put into production.
Rivian has also made a point of showing off rooftop tents at various media events for its vehicles, perhaps also whetting appetites for this latest, brand-official version. It’s the perfect accessory for electric vehicles focused on off-road adventures, complete with a charging network built with that in mind.
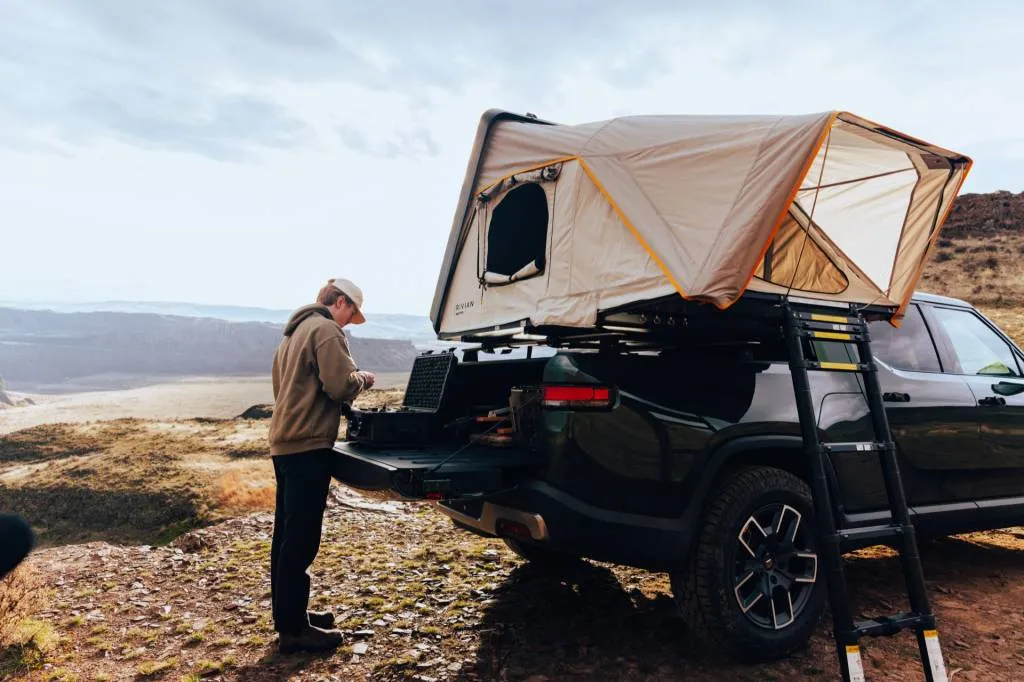

Rivian x iKamper Skycamp Mini rooftop tent
Called the Adventure Network, that charging network is being upgraded with more powerful DC fast-chargers and amenity-filled sites that will be open to all EVs. Rivian also operates Level 2 AC chargers, called Waypoints by the automaker, some of which let owners enjoy tent-based glamping with Under Canvas, which offers a more upscale alternative to traditional camping at popular recreation sites.
More options for off-grid travel are arriving soon—like the Airstream Basecamp 20Xe electric travel trailer that uses a 10.3-kwh battery pack and 3,000-watt inverter to power appliances and electronic devices for those that don’t want to disconnect completely.
